In India we all live happily together, love and conflicts go hand in hand but there are some powers vested in the hand of elders. Being a child we often see parents obey their elders and it goes on.
For instance – In a joint hindu family the hierarchy is like Grandparents are at the top then the elder uncle, parents then elder brother and so on.
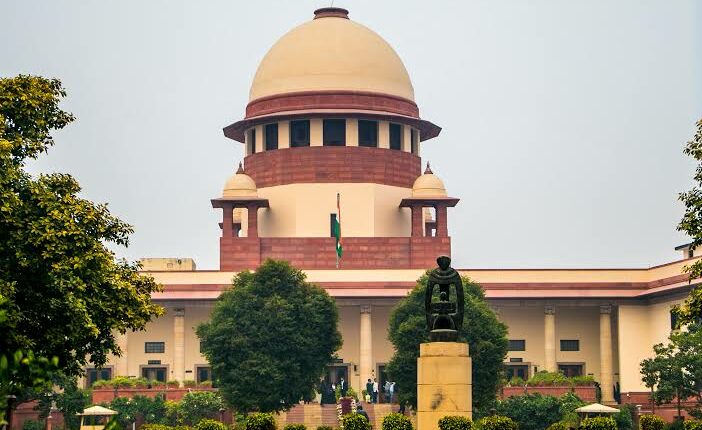
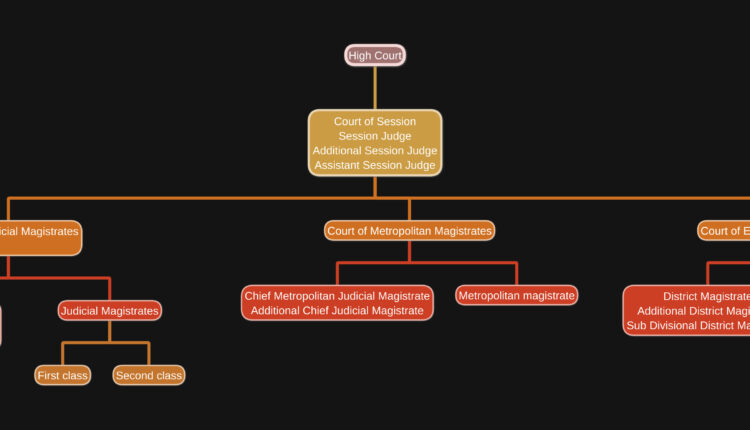
In the same way our judiciary system is also having a hierarchy system where Supreme Court of India is at the top
Supreme Court
The Supreme Court has the highest authority & also known as the Apex Court of the Country where the Chief Justice of India along with 34 other Judges work to serve justice.
When a person is not satisfied with the judgement of district court then can file a plea in High Court and then in Supreme Court.
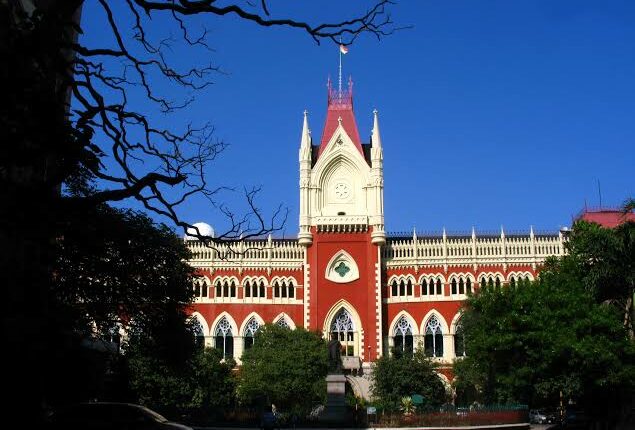
High Court
The High Court is the second authority in the judiciary system. In India there are 25 High Courts with more than 610 judges. There are High Courts constituted in various states for effective and efficient functioning of the judiciary.
Court of session ( Section 9 of CrPC)
The Court of Session is also known as Session Court and is accountable towards the High Court for the functioning in the district.
The High Court appoints Session Judge who is of the highest court in the district then comes additional sessions judge and thereafter Assistant session judge.
Court of Judicial Magistrate ( Section 11 of CrPC)
Judicial Magistrates are classified into two –
Judicial Magistrate first class (having more authority than Judicial Magistrate second class)
Judicial Magistrate second class
Chief Judicial Magistrate (section 12 of CrPC) is appointed from Judicial Magistrate first class. CJM subordinates with Session Judge and Judicial Magistrates subordinates with him.
After Chief Judicial Magistrate, Additional Chief Judicial Magistrate have authority and responsibilities just like Chief Judicial Magistrate. Then comes Sub divisional Judicial Magistrate.
Courts of Metropolitan Magistrates ( section 16 of Code of Criminal Procedure)
In metropolitan areas, the court of the metropolitan magistrate shall be established after consulting the High Court of that State.
Chief Metropolitan Judicial Magistrate is appointed among metropolitan magistrate and after him additional chief metropolitan magistrate functions.
Executive Magistrates ( Section 20 of CrPC)
Executive Magistrates are appointed for performing magisterial functions allocated to the executive. The State Government may appoint them. District Magistrate is appointed among executive Magistrates. After DM, Additional District Magistrate is empowered to take decision thereafter Sub divisional Magistrate.
Everyone in courts of metropolitan magistrate is accountable towards District Magistrate.